Top ten cellular mechanisms that point to Design and Creation
It takes a lot more faith to believe in the theory of evolution than to believe in God.
- Motor proteins transferring cargo. They are 'two-legged' top speed protein complexes that run at microtubules without colliding with each other. Collision prevention is done by coded traffic rules. They can run at huge speed, proportional to cars, 300 km/h (180 mph).
- The MO-1 marine bacteria have seven complex ion flow motors synchronized with a 24-gear planetary gearbox for producing maximum power. They achieve an incredible speed, proportional to human swimming speed, 100 km/h (60 mph). Fine-tunable torque. Forward-backward directions with extremely rapid (1/4 round) change. Efficiency is better than in any human designed electric motor.
- The cell is able to modify DNA bases intentionally along to adaptational needs. This can be done with specific enzymes such as APOBEC3 and A3G. Beneficial DNA alterations are no random changes.
- The cell is able to modify any RNA bases with specific enzymes belonging to APOBEC and ADAR families.
- The cell is able to produce tens of thousands of different proteins by reading one DNA sequence without modifying DNA. This mechanism is called Alternative Splicing.
- Histone code. Histone epigenetic markers represent a biological registry database. DNA is wrapped around histones (compression protein coils), Every histone coil has 8 tails that may carry tens or even hundreds of epigenetic markers. There are over 15 different types of almost atom sized markings. Each marker acts as a memory marker for epigenetic regulation. The histone code is necessary for cellular differentiation. It's inherited by transmission of non coding RNA.
- A/D converters in the cell. There are both analog and digital information in the cell. Methylation profiles are analog information, histone markers are digital information. Some histone markings cause the chromatin to be folded and this affects transcriptional activity.
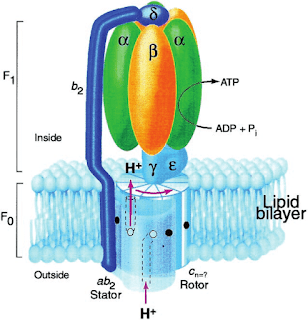
- ATP. Another motor structure in the cell.
- The total volume of DNA of every living taxonomic families is extremely small. It would fit into a mosquito's proboscis.
- DNA repair mechanisms. There are several complex epigenetic driven mechanisms being able to rapidly repair different types of DNA damage. How do those proteins recognize which sequence is not valid? How do they recognize the correct DNA sequence?
- Motor proteins transferring cargo. They are 'two-legged' top speed protein complexes that run at microtubules without colliding with each other. Collision prevention is done by coded traffic rules. They can run at huge speed, proportional to cars, 300 km/h (180 mph).
- The MO-1 marine bacteria have seven complex ion flow motors synchronized with a 24-gear planetary gearbox for producing maximum power. They achieve an incredible speed, proportional to human swimming speed, 100 km/h (60 mph). Fine-tunable torque. Forward-backward directions with extremely rapid (1/4 round) change. Efficiency is better than in any human designed electric motor.
- The cell is able to modify DNA bases intentionally along to adaptational needs. This can be done with specific enzymes such as APOBEC3 and A3G. Beneficial DNA alterations are no random changes.
- The cell is able to modify any RNA bases with specific enzymes belonging to APOBEC and ADAR families.
- The cell is able to produce tens of thousands of different proteins by reading one DNA sequence without modifying DNA. This mechanism is called Alternative Splicing.
- Histone code. Histone epigenetic markers represent a biological registry database. DNA is wrapped around histones (compression protein coils), Every histone coil has 8 tails that may carry tens or even hundreds of epigenetic markers. There are over 15 different types of almost atom sized markings. Each marker acts as a memory marker for epigenetic regulation. The histone code is necessary for cellular differentiation. It's inherited by transmission of non coding RNA.
- A/D converters in the cell. There are both analog and digital information in the cell. Methylation profiles are analog information, histone markers are digital information. Some histone markings cause the chromatin to be folded and this affects transcriptional activity.
- ATP. Another motor structure in the cell.
- The total volume of DNA of every living taxonomic families is extremely small. It would fit into a mosquito's proboscis.
- DNA repair mechanisms. There are several complex epigenetic driven mechanisms being able to rapidly repair different types of DNA damage. How do those proteins recognize which sequence is not valid? How do they recognize the correct DNA sequence?

.jpg)